Cloud security issues refer to the threats, risks, and challenges in the cloud environment. Threats are active attacks that target system weaknesses. Risks include potential damage from cyber threats and vulnerabilities. Challenges are gaps and barriers to attaining good security. To combat these cloud security issues, develop a robust cloud security strategy that addresses all three to provide comprehensive protection.
Table of Contents
4 Top Cloud Security Threats
Cloud security threats are any possible harm that can be done to your cloud systems. When you actively defend cloud assets, you’re protecting them from unintentional or intentional threats that use weaknesses to destroy or steal data. The focus of threat management is mitigating these dangers in order to protect cloud assets effectively. Some of the biggest threats in cloud security are DDoS attacks, cloud storage buckets malware, insider threats, and APT attacks.
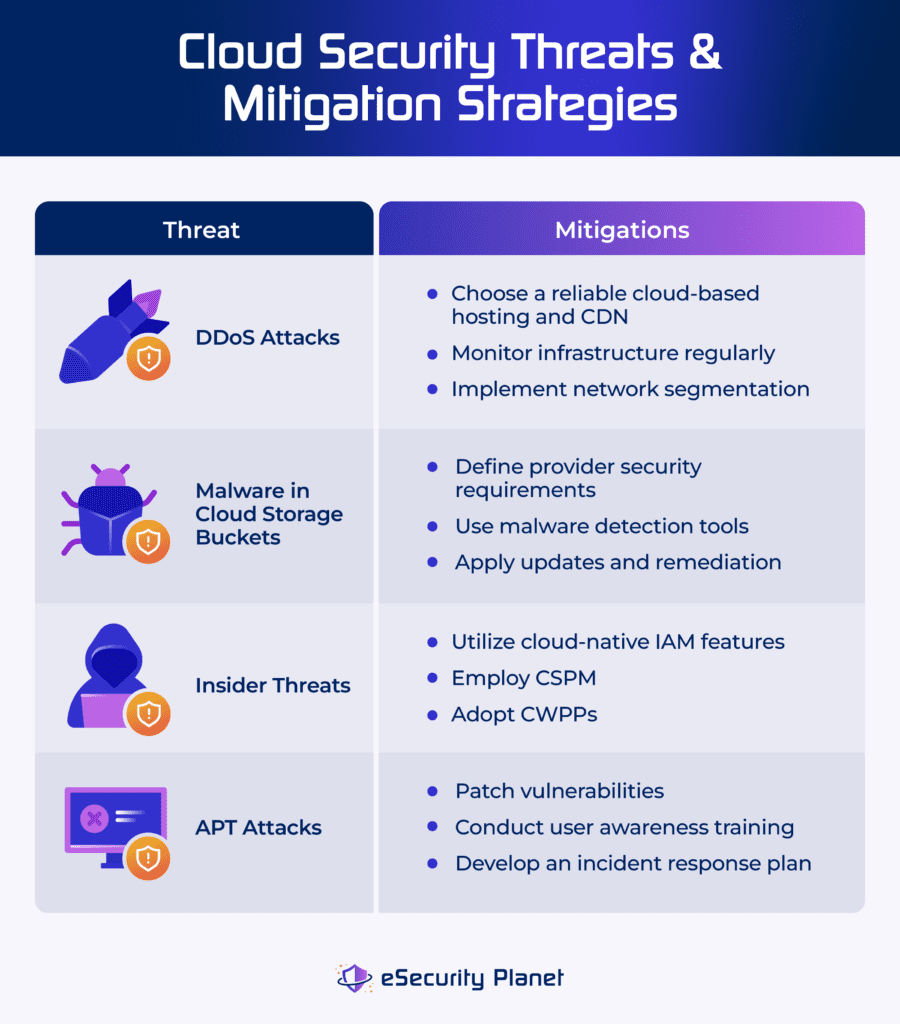
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks
DDoS attacks flood cloud services with excessive traffic, rendering them inaccessible to users. They overwhelm networks or applications with more connections than they can handle, resulting in major disruptions and financial losses. DDoS attacks use several infected devices across multiple networks to establish a botnet. This botnet is a collection of malware-infected machines that coordinate the attack.
Apply the following strategies to mitigate DDoS attacks:
- Select a good cloud-based hosting: Choose a provider with large bandwidth and content delivery networks (CDN). Hide the origin web server’s IP and restrict access with a firewall.
- Monitor infrastructure continuously: Check system capacity, traffic, and essential infrastructure, such as firewalls, on a regular basis to discover irregularities.
- Apply network segmentation: Separate internal and external networks and isolate essential systems to mitigate the impact of assaults.
To help you decide a solution that reduces the impact of DDoS attacks in your organization, explore our buyer’s guide on the best DDoS protection service providers.
Malware in Cloud Storage Buckets
Malware threatens cloud storage buckets due to misconfigurations, infected data, and phishing. It spreads via insecure settings, which enable malicious uploads, unpatched software, susceptible apps, and supply chain assaults involving third-party dependencies kept in these buckets.
Here’s how you can reduce the impact of cloud storage buckets malware:
- Implement malware detection tools: Employ heuristic scanning and signature-based detection for known and unknown malware.
- Set provider security requirements: Only allow access to trusted third-party providers who have a demonstrated track record of security and proper certifications.
- Apply updates and prioritize remediation: Keep your software and dependencies up to date. Prioritize remediation actions according to the sensitivity of the data.
Read our guide on the most secure cloud storage solutions, and discover each solution’s key features, pricing, and benefits.
Insider Threats
Insider threats in the cloud occur when people with authorized access to a company’s cloud services, such as employees, contractors, or partners, abuse their privileges to actively harm the business. This can happen through data sharing or intentional sabotage, such as deleting data or installing malicious software. The cloud’s remote access complicates detection and protection, increasing the potential attack surface.
Lower the risk of insider threats by employing these methods:
- Utilize cloud-native IAM features: Use enhanced identity and access management (IAM) to enforce least privilege access and prevent insider threat vectors.
- Implement CSPM: Employ cloud security posture management (CSPM) systems to recognize threats, misconfigurations, and unwanted access attempts.
- Adopt CWPPs: Apply workload protection platforms (CWPPs) to detect and prevent suspicious activity across all cloud workloads.
Explore our list of the best cloud security companies and vendors to compare the solutions that could help you mitigate insider threats.
Advanced Persistent Threats (APT) Attacks
An advanced persistent threat (APT) is an extended and focused cyber attack in which an intruder gains access to a network while remaining unnoticed. APTs seek to steal critical information and retain long-term access. They’re painstakingly planned and frequently carried out by well-funded groups, who use methods such as spear phishing, zero-day exploits, watering hole attacks, and credential theft to breach high-profile targets.
Try these to prevent APT attacks:
- Patch vulnerabilities immediately: Keep the software up to date by applying patches as soon as possible and executing regular vulnerability scans to identify and fix vulnerabilities before they’re exploited.
- Conduct user awareness training: Incorporate a focused training program into onboarding and workflow process so employees can learn about social engineering strategies, phishing risks, and cloud security best practices.
- Monitor and develop an incident response plan: Employ continuous monitoring to spot suspicious behaviors early on and create a strong incident response strategy to resolve security breaches quickly.
4 Top Cloud Security Risks
A cloud security risk is a combination of the possibility of a threat arising and the system’s vulnerability. Cloud risks include insecure APIs, misconfigurations, cloud concentration, and unmanaged attack surface. Though completely eliminating risks is almost impossible, they can be controlled to remain within a company’s tolerance level through assessments, regulations, and developing plans for the consequences of a threat.
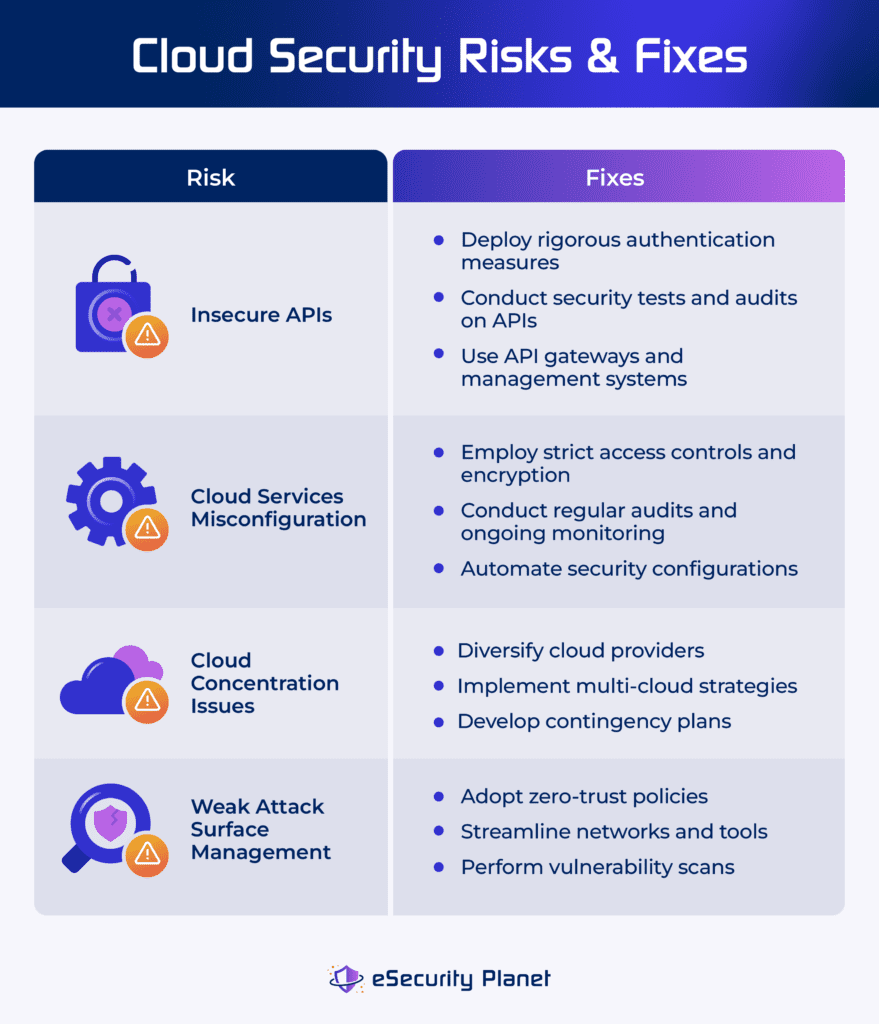
Insecure APIs
Insecure application programming interface (API) in cloud services allows unauthorized access and data breaches. APIs offer seamless integration between cloud services, but if not properly secured, they become points of access for attackers. API security risks may cause weak authentication, input validation, encryption, permissions, error handling, and rate limit issues.
Address insecure APIs through these practices:
- Implement comprehensive security measures: Deploy rigorous authentication, authorization, input validation, and API security testing and monitoring on a continual basis.
- Perform regular security tests and audits on APIs: Quickly detect and address problems using techniques like penetration testing, code reviews, and vulnerability assessments.
- Use API gateways and management systems: Reduce the risk of vulnerabilities in individual APIs by centralizing security features such as authentication, rate limitation, and encryption.
Explore our guide on how to strengthen your API security with the top API security solutions and tools, including their features, advantages, and more.
Cloud Services Misconfiguration
Misconfiguration of cloud services happens when cloud configurations are incorrect, resulting in security breaches and unauthorized access to critical data. It’s a common source of data breaches, which are frequently caused by configuration problems. This exposes sensitive information to the public internet, resulting in reputational damage and financial loss.
To lessen your cloud services misconfiguration risks, implement the following:
- Apply strict access controls and encryption: Employ stringent access control and encryption mechanisms to protect sensitive data from unwanted access.
- Conduct regular audits and ongoing monitoring: Discover and correct misconfigurations using auditing and monitoring solutions.
- Automate security setups: Use automation tools to provide consistent and safe setups across cloud services and lower the risk of human error and misconfiguration.
Delve into our complete guide on cloud configuration management to better understand how it can address misconfiguration in the cloud.
Cloud Concentration Risks
Cloud concentration risk occurs when a company relies excessively on a few key cloud suppliers. This dependence raises the possible disruptions caused by a single provider’s failure. With few options, enterprises confront difficulties in reducing this risk while reaping cloud benefits. Potential effects include widespread event impact, high vendor dependence, which limits technological options, and regulatory compliance failures due to varying restrictions.
These strategies can address your cloud concentration risks:
- Diversify cloud providers: Reduce dependency by distributing risk among several cloud providers and minimize the impact of any single provider’s failure.
- Implement multi-cloud strategies: Distribute workloads and services over multiple cloud platforms to ensure redundancy and resilience to disruptions.
- Develop contingency plans: Create carefully planned continuity plans to quickly address large cloud service outages.
Weak Attack Surface Management
Weak attack surface management occurs when vulnerabilities in a system aren’t detected and mitigated properly. It results from a failure to identify, test, and monitor potential access points, such as devices, users, and software flaws. Impacts include increased risk of data breaches, unauthorized access, and cyberattacks as a result of undetected vulnerabilities, which endanger system integrity, privacy, and the overall security posture.
Resolve weak attack surface management through these tips:
- Adopt zero-trust policies: Limit illegal access by adopting zero-trust security, which ensures that only authorized users can access networks. This lowers entry sites, strengthening the infrastructure against cyber assaults.
- Streamline networks and tools: Remove unnecessary software, program, and equipment, minimize errors, and reduce the attack surface to prevent unauthorized access to your organization’s data.
- Conduct vulnerability scans: Run regular network scans to detect and repair any vulnerabilities, ensuring visibility of the attack surface and protecting both cloud and on-premises networks from exploitation.
Take a look at our in-depth review on the best attack surface management software, their benefits, key features, and pricing.
4 Top Cloud Security Challenges
Cloud security challenges refer to the difficulties that a business faces when protecting its cloud systems against attackers and intrusions. These challenges develop as a result of weaknesses and complexities in the cloud architecture, thus putting your assets at risk. Managing cloud challenges focuses on discovering and fixing issues, particularly during system migration, to ensure robust security measures are in place.
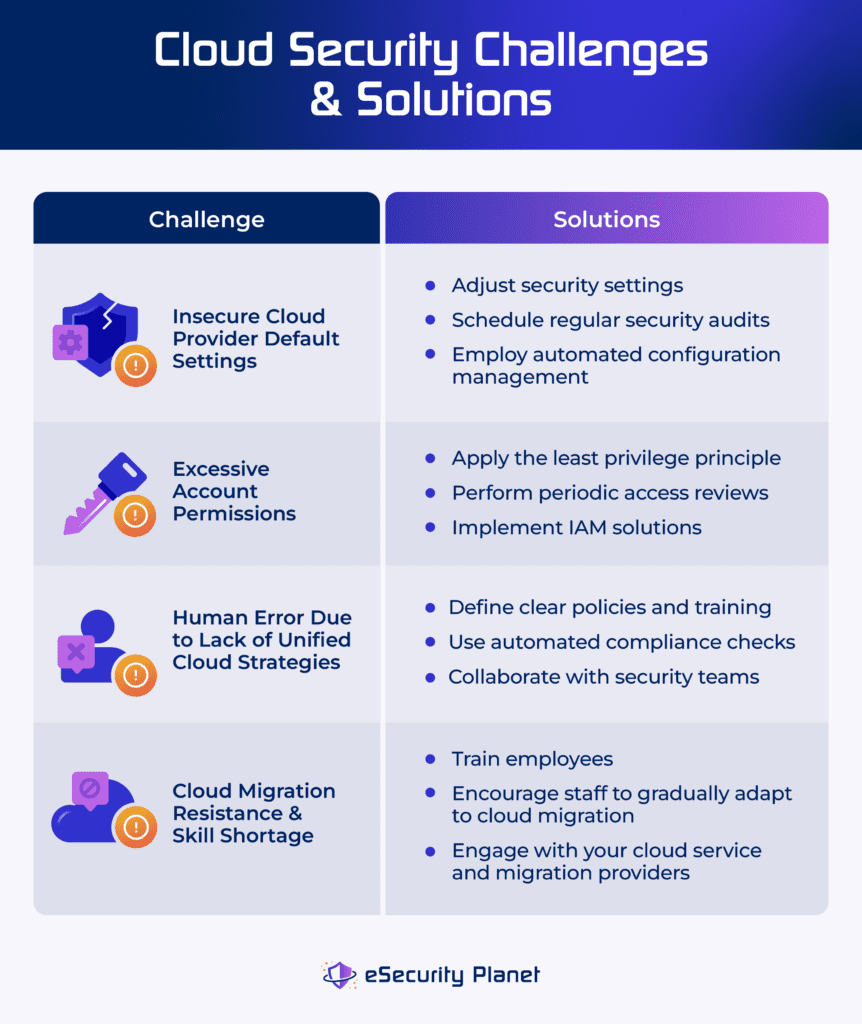
Insecure Cloud Provider Default Settings
Insecure cloud provider default settings occur when an organization’s security rules fail to satisfy its requirements. Crowdstrike’s 2023 cloud risk report discovered that 36% of reported misconfigurations are due to insecure default settings. It may result in public snapshots, open databases, and neglected cloud infrastructure, exposing sensitive data to malicious actors and risking data theft, destruction, or tampering.
Here are the ways to fix insecure cloud provider settings:
- Customize security settings: Adjust the cloud provider’s default settings to meet the organization’s security needs and ensure effective protection against potential vulnerabilities and illegal access.
- Conduct regular security audits: Schedule consistent audits to identify and fix unsafe default settings. Make sure configurations remain in line with security best practices and company rules.
- Employ automated configuration management: Use automated technologies to manage and enforce security configurations. Ensure that security settings are consistent across cloud environments.
Excessive Account Permissions
Excessive account permissions occur when organizations allow user accounts more rights than necessary, thus increasing the risk of security breaches. Attackers who use these privileges can cause significant damage, including data exfiltration, destruction, code modification, lateral movement, persistence, and privilege escalation. This increases the likelihood of security events and jeopardizes system integrity and confidentiality.
Consider these methods to address excessive account permissions issues:
- Implement the least privilege principle: Restrict user accounts to only the permissions required for their duties and roles.
- Conduct regular access reviews: Perform periodic reviews of user permissions to detect and eliminate unnecessary rights.
- Use identity and access management solutions: Implement IAM solutions to consolidate and automate user access management and enforce granular permissions.
See which identity and access management solution offers the most ideal features and strengths for your organization.
Human Error Due to Lack of Unified Cloud Strategies
The lack of unified cloud strategy and human error are interconnected cloud challenges. Human error, such as misconfigurations or inability to adhere to security regulations, is frequently the result of a lack of clear instructions and unified cloud resource management techniques. A fragmented approach to cloud management increases the possibility of human error, as staff may unintentionally miss security measures in the absence of uniform advice and control.
Reduce human error due to lack of unified cloud strategies by performing these practices:
- Provide clear policies and training: Define thorough security policies and provide regular training to staff on cloud security best practices. Lower the chance of human error by monitoring the execution of your cloud policies.
- Implement automated compliance checks: Use automated tools to constantly monitor cloud environments for compliance with security standards. Reducing the impact of human error by adhering to unified tactics.
- Promote cross-functional collaboration: Encourage collaboration among IT, security, and DevOps teams to create unified cloud strategies that prioritize both speed and security. Align goals and lower the chance of fragmented approaches.
Cloud Migration Resistance & Skill Shortage
Resistance to cloud migration is frequently motivated by concerns about unfamiliarity with new technology. Skills gap relates to a scarcity of competent individuals with knowledge in cloud migration. The skills shortage worsens resistance by limiting access to critical cloud skills and impedes the successful adoption and implementation of cloud solutions. This impacts the timeframe and quality of cloud migration, as well as organizational agility and competitiveness.
Apply these approaches to lessen cloud migration resistance and skills shortage in your organization:
- Invest in employee training: Educate your current IT personnel in cloud migration strategies and technology. Provide constant training to ensure that employees are up to date on the newest developments in cloud computing.
- Cultivate internal talent: Allow staff to gradually acquire cloud migration capabilities. Encourage cross-functional collaboration and knowledge sharing to increase departmental expertise.
- Engage in strategic vendor partnerships: Work with cloud service providers and migration suppliers to have access to external knowledge and resources. Utilize vendor support for training, consultation, and guidance throughout the migration process.
How to Build a Robust Cloud Security Strategy
A strong cloud security strategy includes complete measures to address threats, risks, and challenges thoroughly. A solid strategy relies on comprehensive enterprise resources planning, assessment of risks, threat response, and container security methods. Finally, it should address cultural and technical challenges by deploying solutions and training programs that raise security awareness and streamline security operations.
Develop a Comprehensive Enterprise Cloud Strategy Resources
Before shifting to the cloud, develop a comprehensive enterprise cloud strategy and resources to mitigate hazards associated with unauthorized or unreported public cloud use. This strategy offers a secure and regulated transition that aligns with company goals, reducing the risks associated with unapproved cloud practices. Here’s how to start:
- Assess your company’s current cloud security state: Evaluate current cloud usage. Detect any unauthorized or unrecognized deployments, and assess associated risks.
- Define strategic objectives: Set explicit goals and objectives for cloud adoption that are consistent with company priorities and regulatory constraints.
- Develop a management framework: Create policies and procedures to regulate cloud usage, such as provisioning, access control, and compliance.
Implement a Risk Treatment Model
Apply a risk treatment model that includes agility, availability, security, supplier, and compliance domains to assess cloud risks transparently. This model facilitates informed decision-making by thoroughly examining risks and establishing clear security expectations. Addressing vulnerabilities across these areas allows firms to successfully manage cloud risks while also ensuring alignment with overall security objectives. Take the following steps:
- Define risk domains: Tailor each domain to represent specific security concerns and goals for the organization’s cloud environment.
- Assess cloud risks: Use risk assessment tools and procedures to measure and prioritize risks based on their severity and potential consequences.
- Develop mitigation strategies: Implement preventive measures to mitigate high-priority risks, such as improving security processes, creating access controls, and compliance.
Utilize Cloud Security Tools & Solutions
Implement cloud security solutions like cloud workload protection platform (CWPP), Cloud Security Policy Management (CSPM), and Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management (CIEM). These solutions continuously monitor, detect, prevent, and manage sophisticated threats, misconfigurations, identity breaches, and malicious behavior in hybrid and multi-cloud settings. Follow the practices below in order:
- Select proper solutions: Research and select cloud security solutions, such as CWPP, CSPM, and CIEM, that satisfy your specific security requirements.
- Deploy chosen solutions: Implement the recommended security solutions across hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
- Update and maintain tools on a regular basis: Keep your tools up to date to efficiently address new security threats and vulnerabilities.
Compare the differences between CSPM vs CWPP vs CIEM vs CNAPP to assess which cloud security solution is the most suitable for your needs.
Implement Container Security Measures
Container security measures need the deployment of robust tools and mechanisms to detect, evaluate, and respond to threats within containerized environments. This provides the continuous security of containers by recognizing and mitigating threats throughout their lifecycle, from creation to decommissioning. It protects against any breaches or vulnerabilities in the cloud architecture. Apply these security measures:
- Deploy container security tools: Monitor and protect against attacks using specialized security solutions developed for containerized settings.
- Implement container scanning: Run regular scans of container images and deployments to discover vulnerabilities and maintain security compliance.
- Utilize runtime protection: Use runtime security measures to monitor container operations in real time and detect suspicious activities.
Enhance your container security with the best container and kubernetes security solutions and tools.
Maintain Employees’ Cloud Security Awareness
Organizations may empower their employees to make educated decisions and actively contribute to the maintenance of a safe cloud environment by keeping them up to date on cloud security best practices, emerging risks, and new technology. This continuing education ensures that personnel remain aware, adaptable, and prepared to properly address new security problems. Employ these strategies in your organization:
- Include training programs in your security strategy: Create and implement training programs that address practices like data protection, access control, encryption, and threat detection.
- Offer regular workshops: Provide monthly training, webinars, and seminars on cloud security. Keep personnel informed of the newest trends, dangers, and technology.
- Encourage certification and skill development: Urge staff to obtain certifications and engage in skill development programs to improve their cloud security knowledge.
For easier implementation of your cybersecurity training programs, read our review on the best cybersecurity training for employees.
Bottom Line: Prevent Cloud Security Issues with a Solid Strategy
To effectively manage cloud issues, you must carefully assess prevention and remediation methods while keeping budget and risk tolerance in mind. This strategic decision-making should be incorporated into your overall cloud security plan to guarantee a balanced approach to cybersecurity. Cloud issues are inevitable, but you can reduce the harmful impact associated with these risks, threats, and challenges by implementing a solid cloud strategy.
To bridge the gaps in cloud security, DevSecOps tools integrate security for all levels of the workflow, from development to deployment processes. Check out our extensive review on the best DevSecOps tools, covering their use cases, key features, and more.








