Cloud data security refers to the practice of ensuring the safety of digital information stored or processed in cloud settings. It protects data from threats, human error, and unauthorized access using cloud tools, security rules, and access controls. This includes safeguarding data at rest and in motion, minimizing data theft and corruption, and maintaining confidentiality while allowing data access only to the authorized users.
Why Should Organizations Prioritize Cloud Data Security?
Organizations switching to cloud-based storage and services must prioritize cloud data security in order to properly protect critical information. With data spread across numerous cloud environments and accessed from a variety of devices, a cloud-native security solution guarantees strong protection while promoting flexible innovation and compliance with regulations.
Gartner anticipates a major shift in IT investment to the public cloud by 2025, up from 41% in 2022, highlighting the scalability and agility of cloud solutions to protect businesses against the rising data loss threats. The data-intensive and dynamic corporate setups make cloud data security essential for protecting against both new and existing cyberthreats while also maintaining trust, operational integrity, and regulatory compliance.
Consider cloud data security if your company is:
- Dealing with increasing data volume and complexity: As you manage enormous amounts of data across multiple platforms and cloud settings, it becomes more important to protect sensitive information effectively.
- Migrating to cloud or hybrid environments: Make sure your security keeps up with the nature of cloud-based services, applications, and rapid business processes as you move to cloud or hybrid adoption.
- Supporting remote and hybrid workforces: Cloud data security practices allow safe data access from multiple locations and devices while retaining accessibility for remote and hybrid workforce models.
How Cloud Data Security Works
Cloud data security protects sensitive information stored and processed in cloud environments by combining encryption, authentication, access controls, data masking, monitoring, and incident response measures. These precautions protect data security, integrity, and availability while limiting the risks of unauthorized access, data breaches, and cyberattacks.
Security teams work together to develop and maintain effective cloud data security through six general but critical steps: encryption, authentication, access control, data masking, monitoring, and incident response. The effectiveness of cloud data security is heavily dependent on the skills and efforts of these security teams.
Here’s how you and your team can accomplish cloud data security:
- Encryption: The initial step requires the IT security teams to use encryption tools to encode data at rest and in transit using powerful algorithms so that only authorized individuals with decryption keys have access to sensitive information.
- Authentication: Next, the IT security teams are in charge of implementing authentication mechanisms such as passwords, biometrics, and multi-factor authentication (MFA) using identity and access management (IAM) systems.
- Access control: IT security teams then use role-based access control (RBAC) and attribute-based access control (ABAC) to design and implement access control policies based on organizational requirements and regulatory standards.
- Data masking and obfuscation: Data privacy officers and information technology security specialists use strategies to conceal sensitive data pieces by substituting identifiable information with pseudonyms or proxy characters.
- Monitoring and auditing: IT security teams regularly examine logs and audit trails to spot suspicious activity, anomalies, or potential security breaches as soon as possible. This ensures that risks to cloud-stored data are detected and addressed early on.
- Incident response and recovery: Finally, the incident response teams and the IT operations team define protocols for containing security incidents, researching root causes, and quickly restoring data integrity and system functionality.
Understanding the roles played by different security teams in protecting your cloud data is fulfilled through the shared responsibility approach. The model clarifies the fundamental cloud security responsibilities of cloud service providers (CSPs) and consumers. CSPs protect infrastructure and services, while consumers control data, apps, and access. This methodology provides full protection, reduces security gaps, and encourages accountability.
The teams’ expertise, along with proper implementation of best practices, ensures that cloud-based data remains protected against cloud security challenges while leveraging the advantages of secure cloud computing.
Benefits of Securing Cloud Data
Implementing strong cloud data security measures protects sensitive information while simultaneously offering several operational advantages. The security measures ensure that businesses can confidently gain the benefits of cloud computing while adhering to regulations, optimizing resources, and improving overall efficiency.
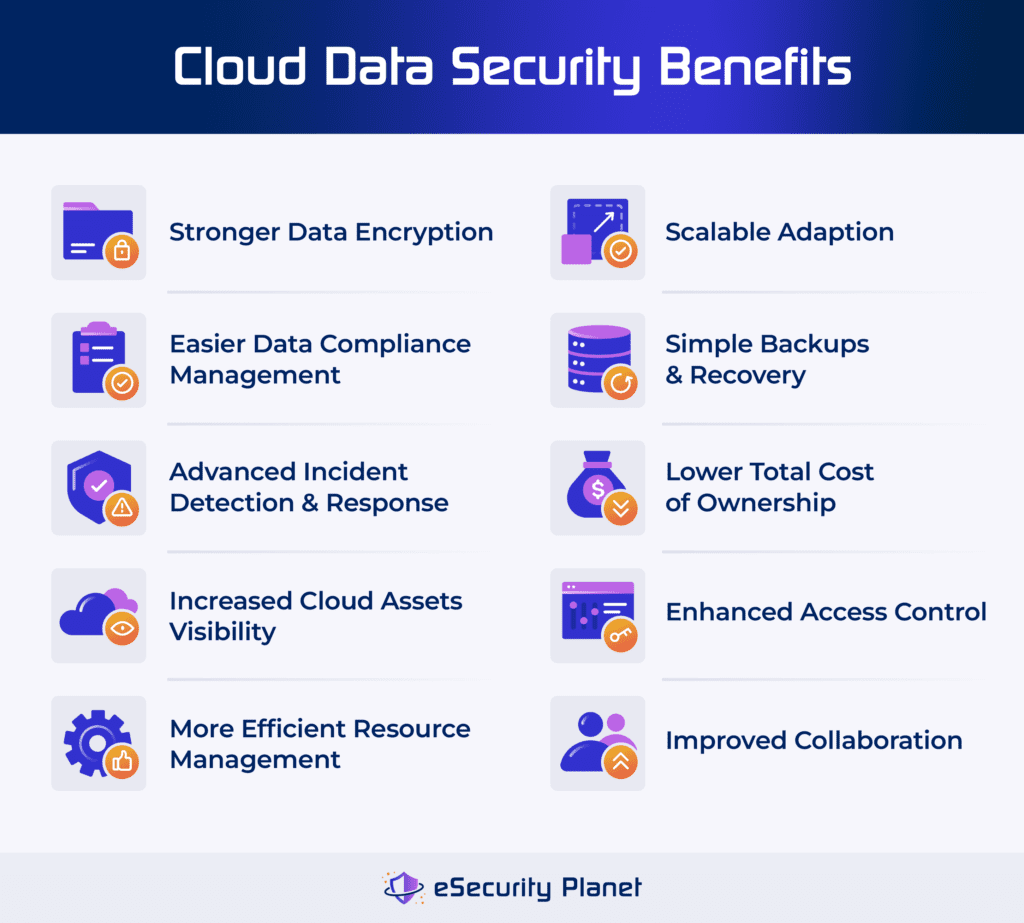
Here are the 10 major benefits of cloud data security:
- Stronger data encryption: Uses modern encryption technologies to protect sensitive data during transit and storage. You can use encryption tools to strengthen confidentiality and security from unauthorized access.
- Easier management of data compliance: Complies with regulations by tracking data storage, access, processing, and protection. Apply data loss prevention tools to lower the likelihood of compliance infractions.
- Advanced incident detection and response: Quickly identifies and responds to security incidents with AI-driven security analytics and automated scanning for suspicious activities, reducing potential damage.
- Increased cloud assets visibility: Monitors and gains insights about your cloud assets, user activity, and data access patterns to ensure transparency and improved control over your data environment.
- More efficient resource management: Assigns infrastructure maintenance to the CSP to save money on IT and free up workers to focus on essential business areas such as customer care and modernization.
- Scalable adaption: Quickly adjusts your cloud resources to match your company demands as they increase. Cloud data security tools enable efficient activity management and cost-effective scaling.
- Simple backups and recovery: Automates backup solutions and standardizes recovery procedures to reduce manual oversight and allow for quick data and application restoration, hence improving business continuity.
- Lower costs: Reduces the total cost of ownership (TCO) by eliminating the need for expensive on-premises infrastructure and employing your cloud providers’ latest security features and capabilities.
- Enhanced access control: Ensures that authorized users may access cloud-hosted databases from any device and place with an internet connection, meeting the needs of today’s digital workforce.
- Improved collaboration: Offers a secure, centralized platform for data exchange and communication so team members can work together seamlessly to increase productivity and collaboration.
Common Challenges of Cloud Data Security
As enterprises adopt cloud and hybrid environments, they experience various data protection challenges. Ensuring strong cloud data security necessitates navigating a complex environment filled with possible risks and compliance challenges. Here are the common issues that businesses encounter when safeguarding data in the cloud:
- Inconsistent coverage: Different levels of coverage and capabilities across several clouds and hybrid environments lead to inconsistency in protection.
- Rising cybersecurity threats: Cloud databases and storage are popular targets for threat actors, especially when businesses adopt new data management techniques.
- Stringent requirements: Implementing security policies across various settings to meet severe data protection regulations can be complex.
- Dispersed data storage: International data storage not only reduces latency and increases flexibility but also creates data sovereignty concerns.
- Increased attack surface: Flexible and scalable cloud infrastructures frequently result in misconfigurations and assets placed outside of security policies.
9 Best Practices for Cloud Data Security
Effective cloud data security practices consist of identifying and categorizing data, applying unified visibility, regulating resource access, encrypting data, deploying DLP, enhancing data posture, monitoring risks, and using a single platform for documentation. By adhering to these best practices, you can build a strong cloud data security architecture that secures sensitive information. They enhance the dependability and integrity of your cloud infrastructure.
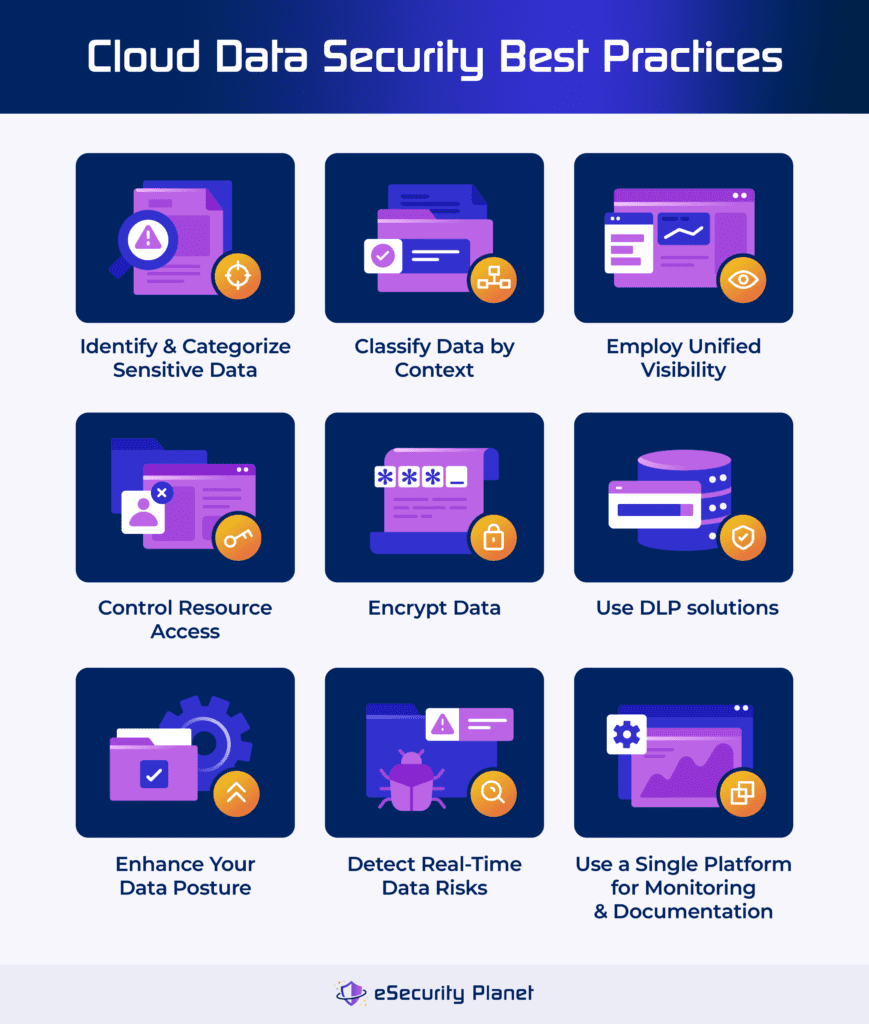
Determine Sensitive Data
Identify and categorize sensitive data from public cloud platforms, virtualization environments, data analytics platforms, and databases. This includes finding “shadow data.” Use automated discovery technologies to examine your whole environment, making sure no data is missed. Regular audits can help keep data inventories up to date.
Categorize Data by Context
Classify data by kind, sensitivity, and control rules. Consider how data goes across the company and how it’s used. Implement data classification policies and tools for labeling and tracking data. Review data classifications on a regular basis to verify they’re up to date and meet compliance standards.
Provide Unified Visibility
Use unified discovery and visibility to detect misconfigurations, vulnerabilities, and threats in private, hybrid, and multi-cloud systems. Employ centralized dashboards and monitoring technologies to acquire complete visibility. Ensure constant monitoring in order to recognize and respond to concerns as they arise.
Regulate Resource Access
Apply role-based access controls (RBAC) and attribute-based access controls (ABAC) to give users the least amount of access required for their position’s responsibilities. Regularly check and update access permissions. Use identity and access management (IAM) technologies to provide strict access constraints.
Encrypt Data in Transit & Data at Rest
To prevent unauthorized access, encrypt sensitive data during transmission and storage. Use strong encryption techniques like TLS for data in transit and AES-256 for data at rest. To maintain security, ensure that encryption keys and protocols are regularly updated.
Deploy Data Loss Prevention Tools
DLP solutions can detect and prevent data leakage or loss during cooperation, compromised systems, or malevolent insiders. Implement DLP tools to monitor data transfer and enforce policies. To reduce inadvertent data leaks, educate personnel about proper data handling methods.
Enhance Your Data Posture
You can utilize data security posture management (DSPM) tools to detect static threats including misconfigurations, deactivated encryption, versioning issues, and unauthorized access. Perform regular scans and assessments of your cloud infrastructure. Use automated methods to discover and close security weaknesses while also ensuring policy compliance.
Monitor Data Risks in Real-Time
The real-time surveillance of dynamic cloud systems can detect new data assets, developing threats, and novel attack tactics. Use modern threat detection and response tools, like SIEM solutions, to assess and manage risks. To keep up with new threats, update threat intelligence on a regular basis.
Implement a Single Platform for Monitoring & Documentation
Combine monitoring, remediation, and documentation into a single platform to provide complete visibility and automatic responses to cloud security issues. Use a unified security management system to consolidate all security activities. Maintain extensive logging and reporting for auditing and compliance purposes.
In addition to the cloud data security–specific measures listed above, read our comprehensive guide and checklist for cloud security best practices.
What Solutions Help Secure Cloud Data?
CWPP, CSPM, CNAPP, IAM, and DLP solutions improve cloud data security by addressing vulnerabilities, enforcing access rules, and securing applications. They protect sensitive data across cloud infrastructures. Integrating these solutions into your cloud data security frameworks allows you to limit risks while also strengthening the security of your cloud data.
Cloud Workload Protection Platform (CWPP)
CWPPs are used to secure cloud-native apps and workloads. They provide visibility into cloud systems by detecting vulnerabilities and managing risks across a variety of platforms, including Kubernetes, serverless architectures, and classic virtual machines. CWPPs reduce the risks associated with cloud-based application deployment by continuously monitoring for threats and guaranteeing compliance with security regulations.
Our recommended solution: Orca Security is a CWPP tool suited for businesses that value comprehensive cloud workload protection and compliance monitoring. It specializes in complex cloud configuration security, with strong vulnerability management and broad visibility across different cloud platforms. You can contact Orca Security sales for custom quotes and free demo requests.
Explore the top CWPP solutions, highlighting each solution’s top features, strengths, pricing information, and more.
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) Tool
CSPM solutions offer security and compliance across all cloud infrastructures. They automate the examination of cloud setups, detecting errors that could expose sensitive data or introduce security flaws. CSPMs enforce security policies, audit trails, and compliance standards so that cloud resources are properly set up and maintained in accordance with industry best practices and regulatory requirements.
Our recommended solution: Palo Alto Prisma Cloud stands out for its flexible deployment choices, robust third-party security and compliance integrations, machine-learning-driven threat detection, and complete code scanning capabilities. It streamlines customization and automation, making it more user-friendly. The Enterprise Edition costs $18,000 for 100 credits and a 12-month membership through AWS Marketplace.
Discover the top CSPM tools, their strengths, use cases, and features in our detailed review.
Cloud Native Application Protection Platform (CNAPP)
CNAPPs secure cloud-native apps throughout their lifecycle. They offer security features like runtime protection, API security, and threat intelligence tailored to cloud environments. CNAPPs enable enterprises to secure applications from development to production. They provide safeguards against developing threats and vulnerabilities specific to cloud-native architectures.
Our recommended solution: Check Point CloudGuard excels at container security and runtime protection by combining CWPP and CSPM. It’s designed for companies that require powerful security for cloud-native apps, with a unified dashboard, policy rules, and both agent and agentless monitoring. It also provides full security across cloud platforms through unified visibility and auto-remediation. CloudGuard costs $625 per month for 25 assets on AWS Marketplace.
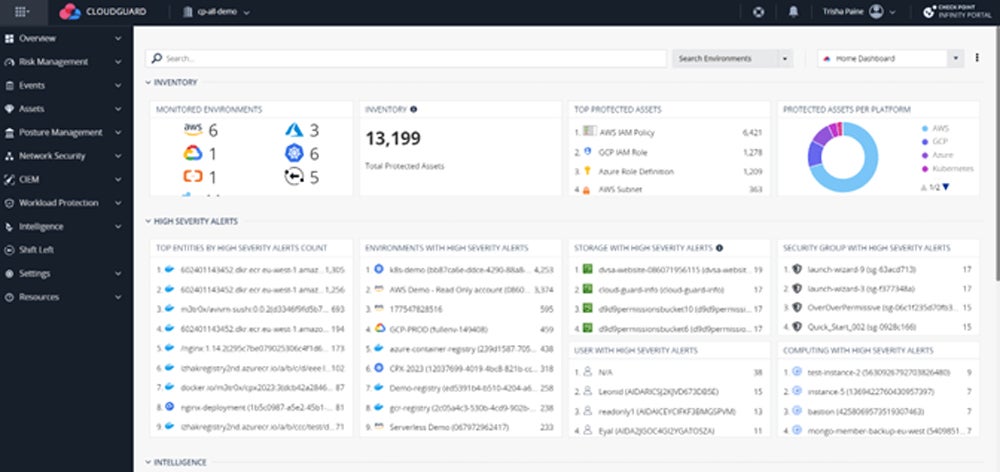
Learn more about the top CNAPP tools available in the market in our comprehensive guide covering their key features, pros, cons, and more.
Identity & Access Management (IAM) Solution
IAM systems manage user identities, permissions, and access rights across several cloud services. They consolidate user authentication processes, impose RBAC controls, and interface with single sign-on (SSO) solutions to improve access management efficiency. IAM enables companies to execute the least privilege principle so that users only access the data required for their tasks. This prohibits unwanted access.
Our recommended solution: JumpCloud is a comprehensive identity, access, and device management tool designed for cloud environments. It offers zero-trust policies, Cloud LDAP for user administration, and Cloud RADIUS for device authentication using certificates. Its Cloud Directory solution centralizes identity control and lifecycle management, making it suitable for both small and large corporations. JumpCloud’s full platform costs $15 per user per month.
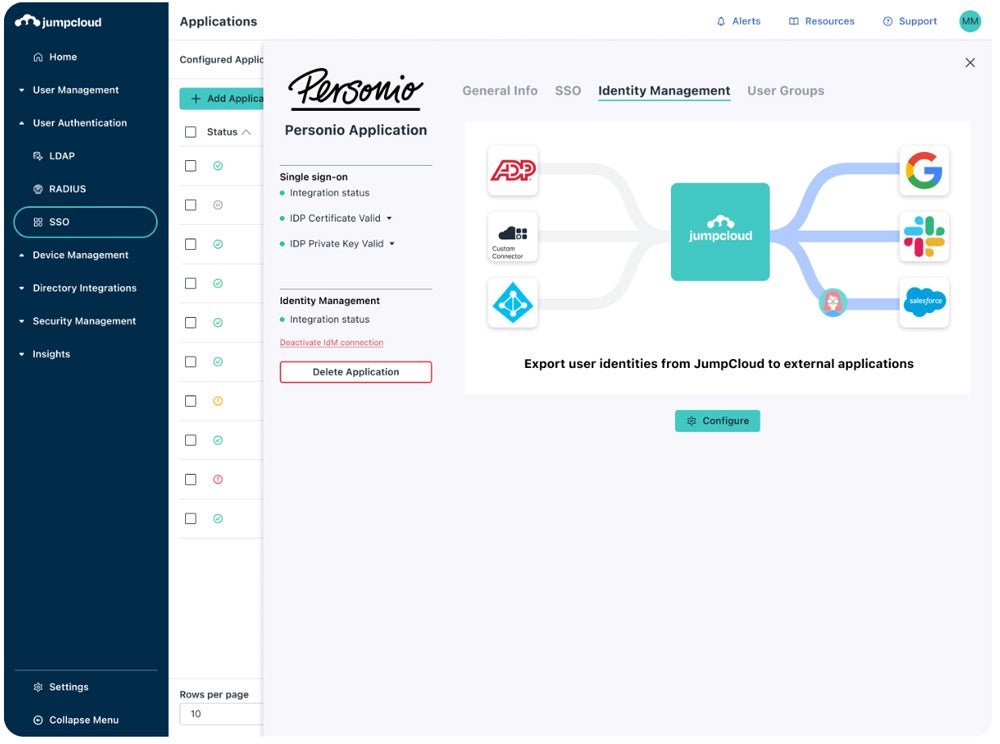
Check out our thorough review of the best IAM solutions, plus their advantages, key features, cost, and ideal use cases.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Tool
DLP systems are crucial for preventing data leaks and maintaining data security in cloud environments. They track and analyze data both in transit and at rest, identifying sensitive information and enforcing regulations to prevent unwanted access, sharing, or loss. DLP solutions provide visibility into data usage patterns, detect abnormalities indicating potential breaches, and allow for quick response measures to manage risks and ensure data integrity.
Our recommended solution: Forcepoint DLP is well-known for its full global policy management across key channels such as endpoint, network, cloud, online, and email. It offers over 1,500 predefined templates and rules to help businesses comply with requirements from 83 countries, making it perfect for large firms. Pricing information is available by contacting Forcepoint’s sales team. They also offer a 30-day free trial for evaluation.
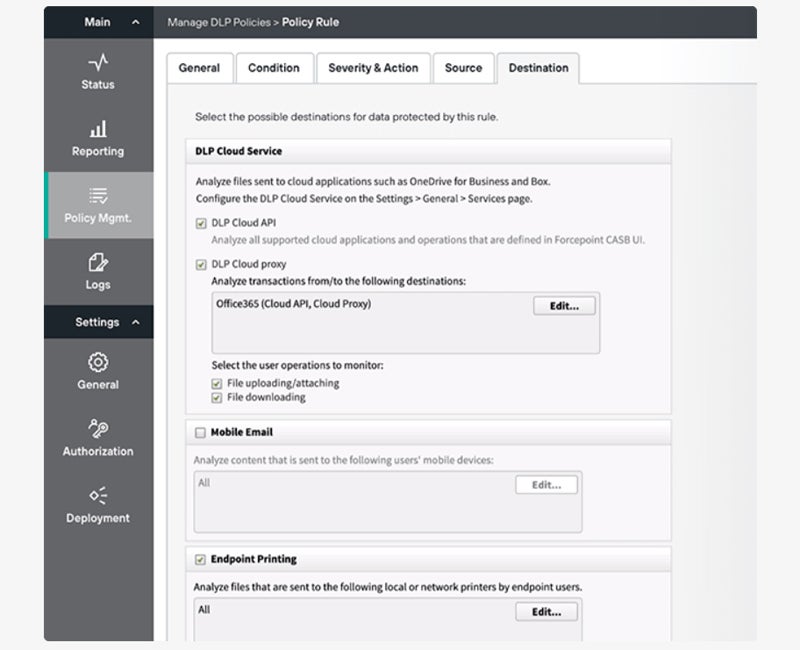
Compare the top DLP solutions in our in-depth guide including their pricing details, key features, strengths, and more.
Bottom Line: Enhance Data Protection with Cloud Data Security
Cloud data security is necessary for enterprises that use cloud-based storage and services. It protects sensitive information in the face of rising data quantities, complicated contexts, and rapid digital transformation. Cloud data security offers plenty of data protection benefits — obtained by applying best practices to properly manage risks. Enhance your protection by implementing these practices along with other cloud security management techniques.
Learn more about the different types of cloud security management in our detailed guide, covering the protection strategies, benefits, challenges, and tools you can use.




