The past week has been a busy one for cybersecurity vulnerabilities, with 34 vulnerable Windows drivers and four Microsoft Exchange flaws heading a long list of security concerns.
Other major flaws appeared in the NGINX Ingress Controller for Kubernetes, Atlassian Confluence Data Center and Server, and Apache ActiveMQ — and the latter two have already been targeted in ransomware attacks.
QNAP vulnerabilities and npm package supply chain attacks also made our list this week, plus a look at the new CVSS v4.0 vulnerability scoring system released last week.
Together, the staggering list of vulnerabilities underscore the need for strong patch and vulnerability management practices — as well as strong cyber vigilance in general.
Oct. 30, 2023
NGINX Ingress Controller for Kubernetes Flaws Can Lead to Credential Theft
Type of Attack: Path sanitization bypass and injection vulnerabilities discovered in the NGINX Ingress controller can allow for credential theft, arbitrary command execution, and critical data access.
The Problem: Three flaws discovered by the Kubernetes security community carry CVSS severity scores of 7.6 to 8.8:
- CVE-2022-4886 (Path Sanitization Bypass): This 8.8-level vulnerability involves a lack of validation, which allows attackers to steal Kubernetes API credentials from the ingress controller, compromise the authentication process by modifying settings, and gain access to internal files including service account tokens.
- CVE-2023-5043 (Annotation Injection, CVSS score 7.6): Ingress-nginx annotation injection allows the execution of arbitrary commands. Attackers can introduce malicious annotations into the ingress controller process, possibly executing unauthorized instructions.
- CVE-2023-5044 (Code Injection): This CVSS score 7.6 flaw allows attackers to use the “nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/permanent-redirect” annotation to inject code into the ingress controller process, which could lead to unauthorized access to critical data.
Ingress controllers are an appealing target for attackers because of their high privilege scope and vulnerability to external traffic.
The Fix: The maintainers of the NGINX Ingress controller have implemented critical fixes and mitigations. v1.9.0 will allow the issues to be mitigated. Ingress Administrators should set the –enable-annotation-validation flag to enforce restrictions on the contents of ingress-nginx annotation fields for CVE-2023-5043 and CVE-2023-5044, while for CVE-2022-4886, for the objects field pathType that defines proxy behavior, admins should enable Exact and Prefix validation by default.
See the Best Container & Kubernetes Security Solutions & Tools
Oct. 31, 2023
Atlassian Warns of Critical Confluence Flaw Leading to Data Loss
Type of attack: CVE-2023-22518 is an incorrect authorization vulnerability that affects all versions of Atlassian’s Confluence Data Center and Confluence Server software.
The problem: The 9.1 severity flaw could allow unauthenticated attackers to delete data. Although the weakness does not undermine confidentiality or allow for data exfiltration, it does represent a serious threat to the integrity of impacted systems. Confluence instances that are available to the general public are particularly susceptible.
Threat actors might use the issue to cause data loss, interrupt operations, and potentially compromise important information. Given the ease with which these vulnerabilities might be exploited, rapid action is required to prevent broad assaults on both government and commercial networks.
Atlassian updated its advisory on Nov. 3 to report that the vulnerability is being actively exploited, which Rapid7 said includes ransomware attacks.
The fix: Atlassian resolved the vulnerability in Confluence Data Center and Server versions 7.19.16, 8.3.4, 8.4.4, 8.5.3, and 8.6.1 and urged admins to upgrade as soon as possible.
If immediate patching isn’t possible for your Confluence instances, you can block known attack pathways by modifying the /<confluence-install-dir>/confluence/WEB-INF/web.xml file as detailed in the advisory, specifically block access to the following endpoints:
- /json/setup-restore.action
- /json/setup-restore-local.action
- /json/setup-restore-progress.action
Atlassian has been hit by a number of security vulnerabilities in recent months.
Nov. 1, 2023
HelloKitty Ransomware Exploiting Apache ActiveMQ Flaw
Type of attack: Apache ActiveMQ remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability, identified as CVE-2023-46604 with a CVSS v3 score of 10.0.
The problem: A security problem in Apache ActiveMQ lets attackers control systems remotely, making them highly vulnerable. Even though a security fix has been available since October 25, many internet-exposed servers are still at risk, and a number of security researchers have reported ransomware attacks exploiting the vulnerability.
The attackers use files disguised as PNG images to spread HelloKitty ransomware, among other attacks. These files contain a .NET program that loads another .NET component named EncDLL, which is in charge of stopping certain processes, locking files, and adding a “.locked” extension to them.
The fix: To fix this critical security problem, administrators must deploy the available Apache security upgrades as soon as possible. Vulnerable versions from 5.15 to 5.18, including Legacy OpenWire Module versions, can be addressed by upgrading to 5.15.16, 5.16.7, 5.17.6, or 5.18.3.
New CVSS 4.0 vulnerability severity rating standard released
Eight years after the release of CVSS v3.0, the Forum of Incident Response and Security Teams (FIRST) has released CVSS v4.0, the latest version of its Common Vulnerability Scoring System standard. CVSS v4.0 improves granularity, eliminates score uncertainty, and simplifies threat metrics.
Additional vulnerability assessment metrics have been added, including Automatable (wormable), Recovery (resilience), Value Density, Vulnerability Response Effort, and Provider Urgency. CVSS v4.0 also adds Supplemental and Environmental safety measurements and values relevant to operational technology (OT), industrial control systems (ICS), and Internet of Things (IoT) contexts.
New nomenclature has been added to stress that CVSS is more than the Base score:
- CVSS-B: CVSS Base Score
- CVSS-BT: CVSS Base + Threat Score
- CVSS-BE: CVSS Base + Environmental Score
- CVSS-BTE: CVSS Base + Threat + Environmental Score
Nov. 2, 2023
34 Windows Drivers Cloud Allow Device Takeover
Type of attack: 34 vulnerable Windows Driver Model (WDM) and Windows Driver Frameworks (WDF) drivers cloud allow complete device control.
The problem: VMware Carbon Black researchers detailed the findings in a blog post. Non-privileged threat actors can exploit these drivers to gain complete device control, execute arbitrary code, modify firmware, and escalate operating system privileges, posing a significant security risk.
Vulnerable drivers like AODDriver.sys, IoAccess.sys, and PDFWKRNL.sys (CVE-2023-20598) allow unauthorized access to critical system components and kernel memory access. Twelve drivers can subvert security mechanisms, while seven enable firmware erasure in SPI flash memory, rendering the system unbootable. Certain WDF drivers can be weaponized by privileged threat actors in a Bring Your Own Vulnerable Driver (BYOVD) attack.
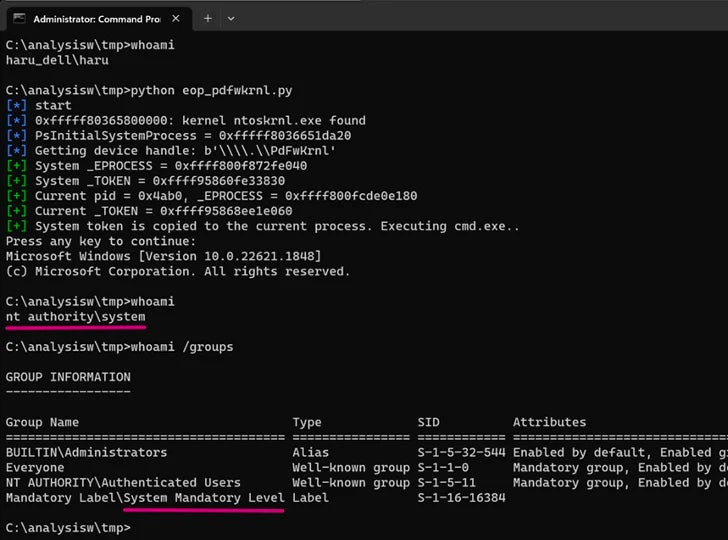
The fix: To address this issue, thorough action is required:
- Driver Patching: Developers and manufacturers of affected drivers must deliver patches and upgrades as soon as possible to address the reported vulnerabilities. Patching is critical for avoiding potential exploitation and device compromise.
- Enhanced Security Measures: End users and organizations should ensure that their systems are equipped with up-to-date security software and methods that can identify and neutralize efforts to exploit these vulnerabilities. Regular system upgrades and security audits are essential for maintaining strong defenses.
- Security Awareness and Training: Educating and training users, particularly those in businesses, on the hazards associated with vulnerable drivers, as well as the significance of upgrading their systems, can help to avoid unintended exploitation. A more proactive approach to system security might result from increased awareness.
- Collaboration: Cybersecurity groups, organizations, and industry stakeholders must work together to exchange knowledge and best practices in order to develop a collective defense against comparable threats. Collaborative initiatives improve the digital ecosystem’s overall resilience.
See the top antivirus software and EDR solutions
New Microsoft Exchange zero-day vulnerabilities enable RCE and data theft attacks
Type of attack: Microsoft Exchange has been hit by four zero-day vulnerabilities, allowing remote attackers to execute arbitrary code or access sensitive information, as reported by Trend Micro’s Zero Day Initiative.
The problem: ZDI-23-1578, ZDI-23-1579, ZDI-23-1580, and ZDI-23-1581 are vulnerabilities in Exchange’s code that include inappropriate validation of user input and URIs. Exploiting these vulnerabilities may result in remote code execution or unauthorized access to sensitive data. While needing authentication for exploitation decreases their severity, fraudsters may access Exchange credentials in a variety of ways, making these vulnerabilities substantial security threats.
The fix: After analyzing the complaints, Microsoft responded that the vulnerabilities had either been fixed or did not satisfy the threshold for immediate service based on their severity categorization rules. The company intends to consider fixing these in future product versions and upgrades as needed. ZDI suggests limiting contact with Exchange applications as a mitigating measure, although this may cause interruptions for organizations. If account credentials are hacked, adding multi-factor authentication can prevent unwanted access.
48 Malicious npm Packages Install Reverse Shells on Developer Systems
Type of Attack: Reported by Phylum researchers, 48 misleading npm packages containing malicious JavaScript code have been discovered installing reverse shells on developer systems, posing a significant threat to developers who unknowingly include these packages in their projects.
The Problem: The authentic appearance of these npm packages makes them hard to recognize, leading developers to unknowingly install compromised packages. Once integrated, these packages execute code that allows unauthorized remote access, compromising the system’s security. The use of obfuscation techniques complicates detection, making it challenging to identify and counteract the threat promptly.
The Fix: Addressing this issue requires a comprehensive approach to enhance open source ecosystem security:
- Enhanced Package Review: Platforms such as npm need rigorous checks to identify suspicious packages before publication. Automated tools can flag potential threats, aiding in the early detection of malicious content.
- Dependency Trust and Verification: Developers should exercise caution when adding dependencies, and relying on trusted sources. Tools ensuring package integrity before installation enhance security.
- Community Vigilance: Active community participation is essential. Collaboration among developers, security experts, and platform maintainers leads to swift detection and removal of malicious content.
- Security Education: Educating developers about third-party package risks and promoting secure coding practices is vital. It reduces the likelihood of falling victim to such attacks, ensuring the software supply chain’s integrity and security.
See the Top Application Security Tools & Software
Nov. 4, 2023
QNAP Warns About Major Command Injection Problems in QTS OS and Applications
Type of attack: CVE-2023-23368 and CVE-2023-23369 could allow remote attackers to execute instructions over the network, posing a serious security risk.
The problem: The flaws affect several versions of the QTS operating system, QuTS hero, and QuTScloud. Exploiting these issues might result in unauthorized command execution, exposing NAS systems to data theft, encryption, or ransomware attacks. The potential impact on sensitive data integrity is substantial given the nature of NAS devices as data storage systems.
The fix: QNAP Systems has patched the vulnerabilities and reported the fixed versions in its advisories (CVE-2023-23368 and CVE-2023-23369). Administrators should upgrade their systems as soon as possible.
Last week’s vulnerability roundup: Weekly Vulnerability Recap – October 30, 2023 – Citrix & Cisco Haunted by Vulnerabilities




