A virtual private network (VPN) does more than just mask your identity—it fundamentally changes how your data moves across the internet. But what’s really going on under the hood when you browse the web using a VPN? Understanding this can be crucial for IT managers and professionals who are keen on maintaining robust cybersecurity practices.
In this article, we’ll explain how a VPN works, explore its encryption mechanisms, review common VPN protocols, and discuss its various business applications.
Featured PartnersFeatured Partners: Cybersecurity Software
eSecurity Planet may receive a commission from merchants for referrals from this website
How a VPN Works
A VPN works by creating a secure, encrypted connection between your device and the internet. This process involves multiple steps and technologies working together to ensure your data remains private and secure. Here are the steps of VPN functionality:
Step 1: Device Connection to a VPN Server
When you activate a VPN on your device, it first connects to a VPN server. This server is usually located in a different geographical location, which could be chosen by you or automatically by the VPN service.
Step 2: Data Encryption
Before your data leaves your device, the VPN client software encrypts it using advanced encryption protocols. This encrypted data is nearly impossible to intercept and read without the appropriate decryption key.
Step 3: Data Transmission to the VPN Server
The encrypted data is then transmitted to the VPN server. This server acts as an intermediary between your device and the wider internet.
Step 4: IP Address Masking
The VPN server replaces your original IP address with its own. This means that when your data reaches the destination server (like a website), it appears as if the request is coming from the VPN server’s location rather than your actual location.
Step 5: Data Decryption
When the VPN server receives data from the internet (such as a webpage you requested), it encrypts the data before sending it back to your device.
Step 6: Final Decryption
Your VPN client decrypts the data received from the VPN server, allowing you to access the content as if you were directly connected to the internet.
This process ensures that your internet service provider (ISP), the websites you visit, and any potential eavesdroppers cannot see your real IP address, the websites you access, or the data you send and receive. Instead, they only see the VPN server’s IP address and encrypted traffic.
Check out the figure below for a simpler image of how a VPN works:
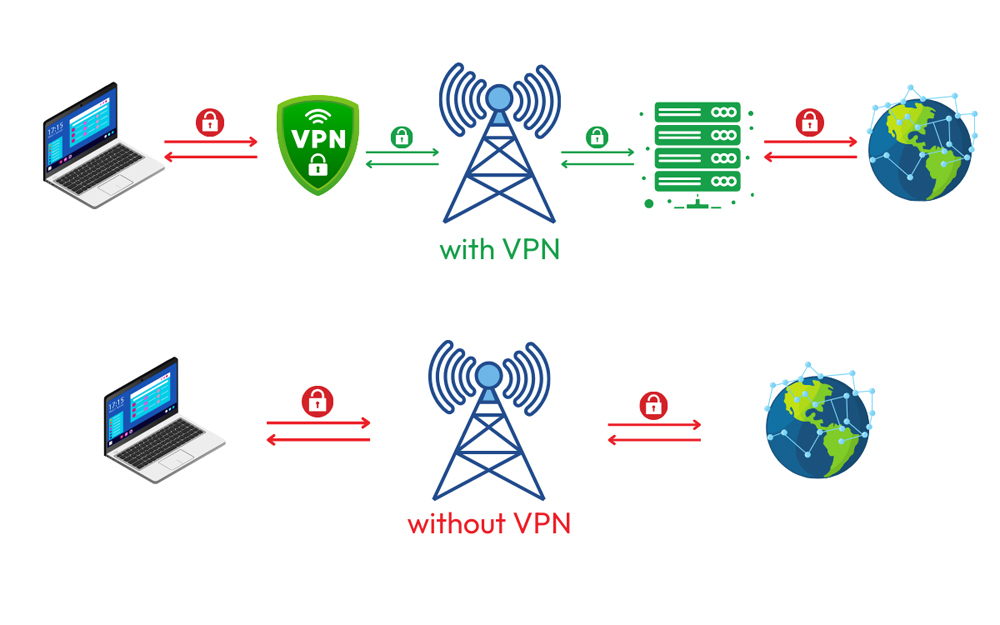
For more information on how to get a VPN, check out this guide.
VPN Encryption Explained
VPN encryption involves converting your data into an unreadable format for anyone who might intercept it. This process ensures that even if someone manages to capture your data, they won’t understand it without the proper decryption key. Here’s a closer look at what VPN encryption entails:
Data Encryption Process
- Encryption algorithm: VPN encryption uses algorithms to transform readable data into an encrypted format. These algorithms are mathematical formulas that scramble the data in a way that can only be reversed by someone with the correct decryption key.
- Encryption key: The encryption key is a string of data used by the algorithm to encrypt and decrypt your data. For example, if a message is encrypted with a key, only someone with that key can decrypt and read the message.
Types of Encryption
Understanding the types of encryption helps you choose the right encryption approach for your data protection strategy. Here’s a closer look at symmetric and asymmetric encryption and their respective roles in securing information.
| Symmetric Encryption | Asymmetric Encryption |
|---|---|
| This method uses the same key for both encryption and decryption. The sender and receiver must both have the same key, which can be a security risk if the key is intercepted. Common symmetric encryption algorithms include AES (Advanced Encryption Standard). | Also known as public-key encryption, this method uses a pair of keys: a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption. The public key can be shared openly, but the private key is kept secret. RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) is a well-known example of asymmetric encryption. |
Encryption Protocols
- AES (Advanced Encryption Standard): AES is a symmetric encryption algorithm used widely in VPNs. It is known for its strength and efficiency, with AES-256 providing the highest level of security.
- RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman): RSA is often used to encrypt data exchanges rather than the data itself. It secures the transmission of encryption keys between parties.
- SHA (Secure Hash Algorithm): While not an encryption method, SHA creates a unique hash of data, which helps verify its integrity and ensures that it has not been altered.
Encryption in Action
- When you connect to a VPN: As soon as you establish a connection to a VPN server, your device encrypts your data before sending it over the internet. This encrypted data is transmitted to the VPN server, where it remains secure.
- From the VPN server: The VPN server decrypts the incoming data from the internet, then re-encrypts it before sending it back to your device. Your device decrypts this data, allowing you to view the content as intended.
Key Components of a VPN Protocol
A VPN protocol ensures secure and efficient data transmission. Its key components, including encryption, authentication, tunneling, and data integrity, all work together to protect your online activity. Here’s a brief overview of how these elements contribute to a secure VPN connection.
- Encryption: The protocol determines the type of encryption used to secure data. Stronger encryption ensures better security but may impact connection speed. Common encryption methods include AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) and RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman).
- Authentication: VPN protocols also manage how your device authenticates its identity to the VPN server. Authentication ensures that data is sent to and received from the correct source.
- Tunneling: VPN protocols establish a secure “tunnel” through which your data travels. This tunnel is an encrypted pathway between your device and the VPN server, protecting your data from interception.
- Data Integrity: Protocols include methods to verify that the transmitted data has not been tampered with during transit. This ensures the integrity and authenticity of the data received.
6 Common Types of VPN Protocols
VPN protocols dictate how your data is transmitted over the VPN connection. Different protocols offer varying levels of security, speed, and compatibility. Here are some of the most common ones and what they bring to the table:
1. OpenVPN
OpenVPN is one of the most popular and widely used VPN protocols, known for its balance of speed, security, and reliability. It’s an open-source protocol, which means it is constantly being reviewed and updated by the global security community.
Strengths:
- Security: OpenVPN uses strong encryption standards, including AES-256, and supports a variety of cryptographic algorithms. It also offers robust authentication options and is highly configurable.
- Flexibility: It works across multiple platforms, including Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, and iOS, making it highly versatile.
- Performance: While OpenVPN is secure, it may require more processing power, potentially slowing down connections on less powerful devices.
Use Cases:
OpenVPN is ideal for users prioritizing security and privacy, such as those accessing sensitive information or bypassing strict censorship.
2. L2TP/IPsec (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol)
L2TP (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol) is often paired with IPsec (Internet Protocol Security) to provide encryption and secure data transmission. This combination is a common VPN protocol that balances security and performance well.
Strengths:
- Security: L2TP itself does not provide encryption, but when combined with IPsec, it offers robust security with double data encapsulation.
- Compatibility: It is built into most modern operating systems, making it easy to set up without needing additional software.
- Stability: L2TP/IPsec offers stable connections, making it reliable for most internet activities.
Use Cases:
This protocol is suitable for those who need a balance between security and ease of use, such as general internet browsing or accessing work networks remotely.
3. IKEv2/IPsec (Internet Key Exchange Version 2)
IKEv2 is a VPN protocol developed by Microsoft and Cisco, often paired with IPsec for encryption. It’s known for its speed and ability to quickly re-establish connections, making it a preferred choice for mobile users.
Strengths:
- Security: IKEv2/IPsec provides strong encryption and supports many cryptographic algorithms, making it secure against most security threats.
- Speed: It’s highly efficient, offering fast connection speeds with low latency, even over mobile networks.
- Stability: IKEv2 is excellent at maintaining a stable connection, especially when switching between networks, such as from Wi-Fi to mobile data.
Use Cases:
Ideal for mobile users who need a fast, secure, and reliable VPN connection, particularly when on the move.
4. PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol)
PPTP is one of the oldest VPN protocols, developed by Microsoft in the 1990s. While it is known for its fast speeds, its security is considered weak by modern standards.
Strengths:
- Speed: PPTP is less resource-intensive, offering fast connection speeds making it suitable for activities like streaming.
- Compatibility: It’s supported on most devices and operating systems, making it easy to set up.
Weaknesses:
- Security: PPTP uses outdated encryption standards, making it vulnerable to modern hacking techniques.
- Reliability: It’s more prone to being blocked by firewalls than other protocols.
Use Cases:
Best for users who prioritize speed over security, such as streaming content in regions with less stringent privacy requirements.
5. WireGuard
WireGuard is a newer VPN protocol that is gaining popularity for its simplicity, speed, and strong security features. It’s designed to be more efficient and easier to implement than older protocols.
Strengths:
- Security: WireGuard uses state-of-the-art cryptography, providing a very high level of security with fewer vulnerabilities.
- Performance: It’s extremely fast, with a lean codebase for quick connections and low latency.
- Simplicity: WireGuard is easier to configure and deploy, making it more user-friendly than some older protocols.
Use Cases:
Ideal for users who want a modern, fast, and secure VPN experience, particularly in scenarios where performance is critical.
6. SSTP (Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol)
SSTP was developed by Microsoft and is integrated into the Windows operating system. It’s known for bypassing firewalls, as it uses the HTTPS port 443, which is rarely blocked.
Strengths:
- Security: SSTP offers robust security, with support for SSL/TLS encryption, making intercepting difficult.
- Firewall bypassing: Its use of the HTTPS port makes it excellent at getting through firewalls that block other protocols.
- Integration: SSTP is deeply integrated into Windows, making it easy to set up and use on Microsoft platforms.
Use Cases:
Best for Windows users who need a reliable, secure VPN that can bypass restrictive firewalls, especially in corporate or public environments.
Each VPN protocol offers distinct advantages and disadvantages, making them suitable for different use cases. Whether you prioritize speed, security, or compatibility, understanding these six common VPN protocols can help you choose the right one for your needs. Whether streaming content, accessing sensitive information, or maintaining a secure connection, selecting the appropriate VPN protocol is key to optimizing your online experience.
How Businesses Leverage VPNs for Enhanced Security
Businesses utilize VPNs for various purposes beyond individual privacy. Here are some common use cases:
Secure Remote Access
VPNs allow employees to securely connect to the company’s internal network remotely. This is crucial for protecting sensitive company data, especially when employees are working from home or traveling.
Bypassing Geo-Restrictions
For businesses with operations in multiple countries, VPNs can be used to bypass geo-restrictions on websites or services, ensuring that employees have access to the necessary resources regardless of location.
Enhanced Security for Remote Work
In today’s work-from-anywhere environment, VPNs provide additional security for remote workers, safeguarding sensitive communications and reducing the risk of data breaches.
Cost-Effective Network Security
For small and medium-sized enterprises, deploying a VPN can be a cost-effective alternative to expensive types of network security solutions. It enables secure communication without the need for dedicated hardware.
Anonymous Market Research
Businesses often use VPNs to conduct market research anonymously. They can gather competitor information without revealing their identity or location by masking their IP addresses.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Does a VPN Hide Your Location?
Yes, a VPN masks your real IP address with the IP address of the VPN server you’re connected to. This hides your location from websites, services, and potentially malicious actors.
Can Someone Find Out That You’re Using a VPN?
While your activities are hidden, someone (e.g., your ISP or network administrator) can detect you using a VPN. VPN traffic has distinct characteristics, such as encrypted data and connections to known VPN servers.
Is Using a VPN Legal?
Yes, using a VPN is legal in most countries. However, some countries with strict internet regulations may restrict or outright ban VPN usage. Always check local laws before using a VPN.
Bottom Line: Secure Your Business with VPNs
A VPN is a powerful tool that secures your internet connection by encrypting your data and masking your IP address. It is essential for IT professionals to understand how it works, as it helps select the right VPN solutions for business needs and personal use.
You can check out our guide on enterprise VPN solutions for more information. If you want to learn more about VPN security, visit our detailed overview. Stay informed on the latest network security threats and best practices with our comprehensive network security threats guide.




